이론
암호학 중심 이론 정리
https://verybigsilver.tistory.com/55
[암호학 둘러보기](8)[RSA]
RSA: 비대칭키 암호화 방식디피-헬만과는 다르게 서명까지 지원해 안전함. (상대방의 공개키를 이용해 암호화하기 때문)과정메세지 보내는 A, 메세지 받는 B이고 공개된 파라미터 e가 있다.B의 공
verybigsilver.tistory.com
수론 중심 이론 정리
https://verybigsilver.tistory.com/100
참고
구현
일단 코드를 대충 짜면 이렇게 된다.
def extended_gcd(a, b):
if b == 0:
return 1, 0 # 해는 (1, 0)
x1, y1 = extended_gcd(b, a % b) # 재귀 호출
x = y1
y = x1 - (a // b) * y1
return x, y
# user parameter
# p, q는 소수
p = 73
q = 97
msg = 1615
m = p*q
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
k = 1789
print("공개: ", m, k)
# encoding
Ciphered = msg**k%m
print(Ciphered)
# decoding
u, v = extended_gcd(k, phi)
DeCiphered = Ciphered**u%m
print(DeCiphered)위 코드에서는 p, q, k를 직접 정해줘야 한다.
이걸 자동화 하고 암호화와 복호화를 다른 파일에서 하게 했다
#Cipher
import random
import time
# ax+by=1 해 구하는 함수
def extended_gcd(a, b):
if b == 0:
return 1, 0 # 해는 (1, 0)
x1, y1 = extended_gcd(b, a % b) # 재귀 호출
x = y1
y = x1 - (a // b) * y1
return x, y
# 소수 판정 함수
def is_prime(x):
if x < 2:
return False
for i in range(2, int(x**0.5) + 1):
if x % i == 0:
return False
return True
# n 이상의 가장 작은 소수 찾는 함수
def next_prime(n):
while True:
if is_prime(n):
return n
n += 1
# 서로소 판정 함수
def is_coprime(a, b):
def gcd(x, y):
while y:
x, y = y, x % y
return x
return gcd(a, b) == 1
# phi와 서로소인 k값 정하는 함수
def random_coprime(n, phi):
while True:
k = random.randint(2, n-1) # 1은 너무 허접하니까 패스♡
if is_coprime(k, phi) == 1:
return k
# 랜덤으로 소수 p, q 만드는 함수
def random_p_q(hardness):
rand_p_start = random.randint(1, hardness)*hardness # (0~hardness-1까지 무작위 수 뽑기)
rand_q_start = random.randint(1, hardness)*hardness
p = next_prime(rand_p_start)
q = next_prime(rand_q_start)
return p, q
random.seed(time.time())
# parameter
hardness = 10 # 암호의 난도
msg = (int)(input("보낼 메세지(숫자)를 입력하시오: "))
p, q = random_p_q(hardness)
m = p*q
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
k = random_coprime(hardness, phi)
print("공개 파라미터\nm = %d, k = %d" %(m, k))
# encoding
Ciphered = msg**k%m
print("암호문 = ",Ciphered)#Decipher
def extended_gcd(a, b):
if b == 0:
return 1, 0 # 해는 (1, 0)
x1, y1 = extended_gcd(b, a % b) # 재귀 호출
x = y1
y = x1 - (a // b) * y1
return x, y
def prime_factor(m):
for i in range(2, int(m ** 0.5) + 1):
if m % i == 0:
return i, m // i
return None # 소수인 경우 -> 실패
# parameter
m = (int)(input("m값 입력: "))
k = (int)(input("k값 입력: "))
Ciphered = (int)(input("암호문 입력: "))
# decoding
# phi를 구하기 위해 소인수 분해를 해야 됨...
p, q = prime_factor(m)
phi = p*q - (p+q) + 1
u, v = extended_gcd(k, phi)
u = u%phi # <- u가 음수인 경우 처리
DeCiphered = Ciphered**u%m
print("복호문 = ", DeCiphered)hardness에 따라 소수의 크기가 커지므로 더 어렵게 된다.
실제 프로그램을 돌려보면
hardness = 10일때
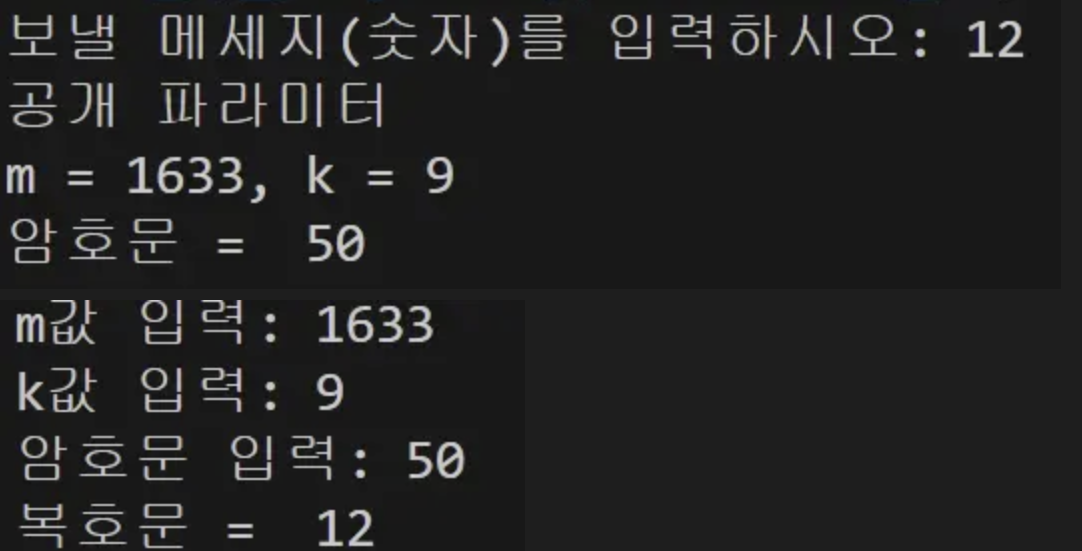
금방 복구된다.
걸리는 시간도 출력하게 코드를 수정하고
hardness 에 따라 복구되는 시간을 보면,
| hardness | 시간 (파이썬) | 시간 (c) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 0.1904008388519287 초 | 0.000000 초 |
| 70 | 0.9146127700805664 초 | 0.000000 초 |
| 100 | 인내심의 한계 | 0.000000 초 |
| 300 | 인내심의 한계 | 0.001000 초 |
| 500 | 안함 | 오버플로우 |
솔직히 파이썬이 많이 느리긴 해서 그냥 c로 옮겨서 더 돌려봤다.
그리고 큰 숫자에 대해서는 오버플로우 등의 이유로 제대로 복호화가 안될 수도 있으니 숫자는 항상 넉넉하게 잡아놓아야 한다.
근데 내가 사용하는 visual studio는 unsigned long long이 제일 큰 숫자라서 hardness가 500이상이면 오버플로우가 난다.
728x90
반응형
'암호학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [암호학](-)[RSA 구현 3] (0) | 2025.04.25 |
|---|---|
| [암호학](-)[RSA 구현 2] (0) | 2025.04.22 |
